Arguments for a possible
based on Evidence from fine arts
Since the sources from the Renaissance themselves do not contain any specific set of instruments to be used, the music presented here is recorded in up to six different instrumentation variants. The assumptions on which the various instrumentation decisions are based shall be clarified here.


zwischen geistlichen und weltlichen Traditionen
It makes sense to have instruments with a similar tonal homogeneity of vocal ensembles for wich the music was developed for. Ensembles limited to one family of the instruments were known as consorts.


an instrument family close to singing
Recorders have been established with the Renaissance. In the recordings use Soprano, Alto, Tenor and Bass-recorder are used in the consort.
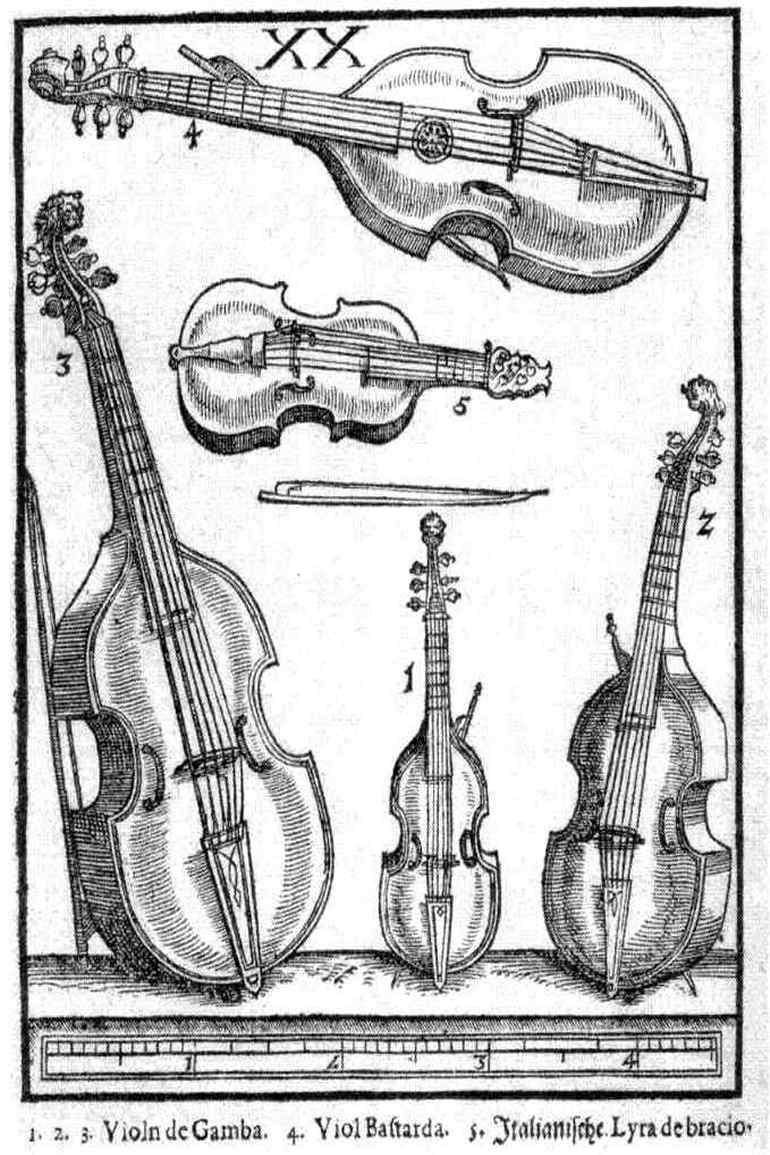
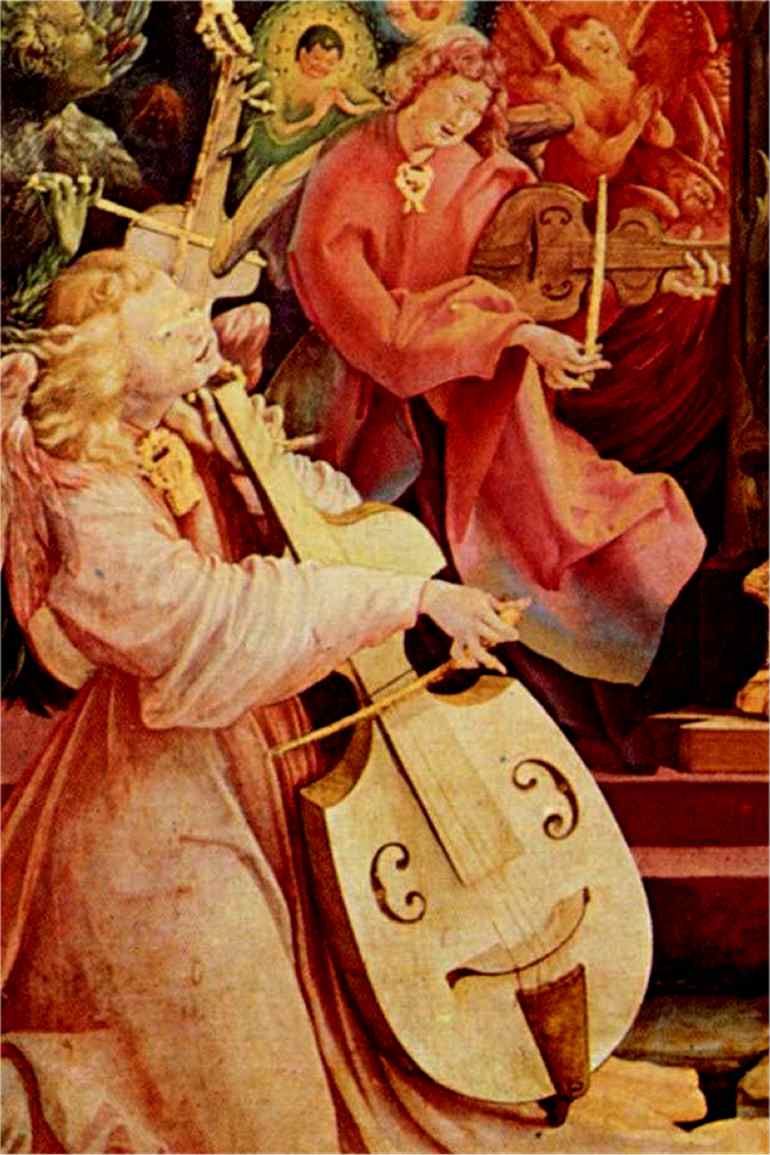


Streichinstrumente der Renaissance
Since in the early Renaissance for the alto and tenor register only a single instrument, the tenor viol, was used ,the recordings use a combination of a bass viol and two different tenor viols, which are occasionally combined for higher registers with a fidule to form a string consort.
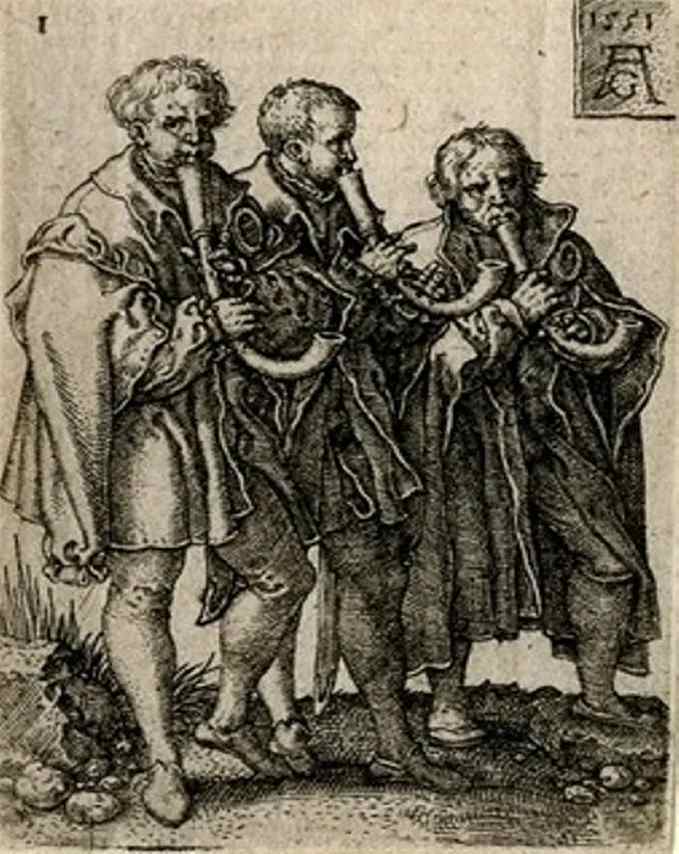
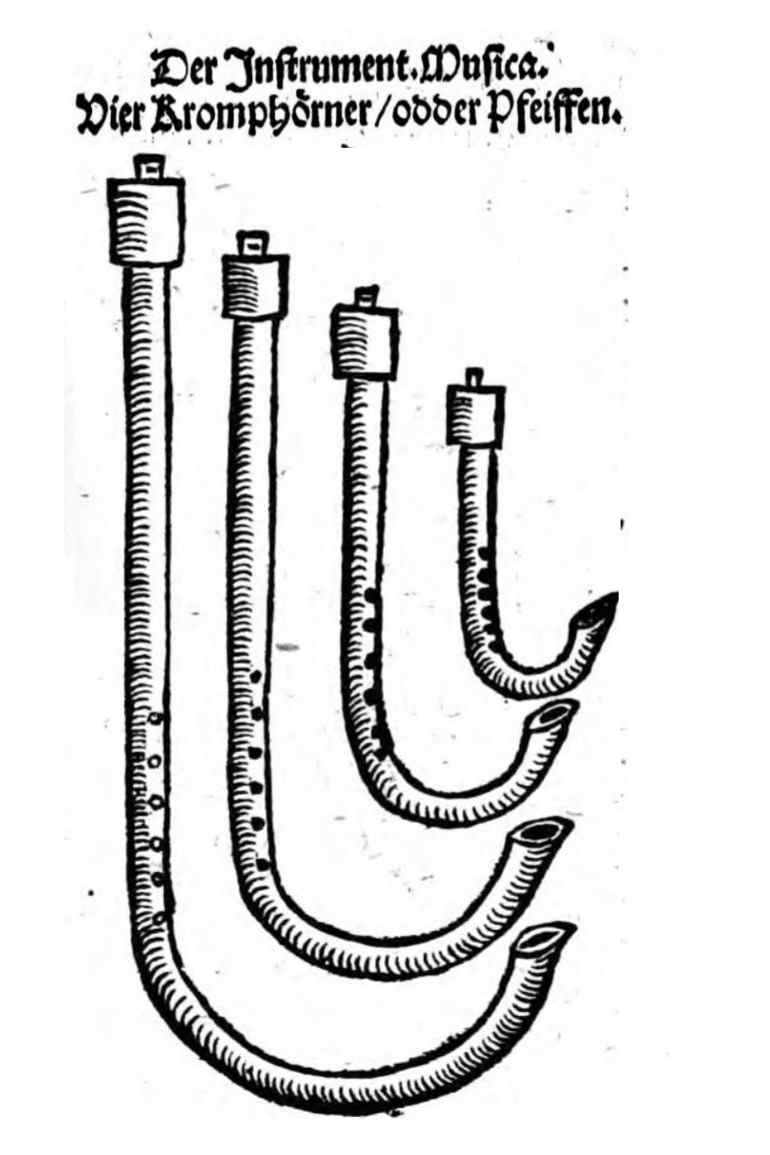

Double reed instruments of the Renaissance
The Krummhömer, common up to the transition from the Renaissance to the Baroque, are used in the consort in soprano, alto, tenor and bass range.


Blechbläser-Ensembles
In order to achieve a homogeneous sounding brass ensemble with period instruments, natural trumpets and sackbutts are combined in the recordings.
Mixed ensembles, so-called "broken consorts", also use the following additional melody instruments, each of which only takes over individual voices of a musical set.
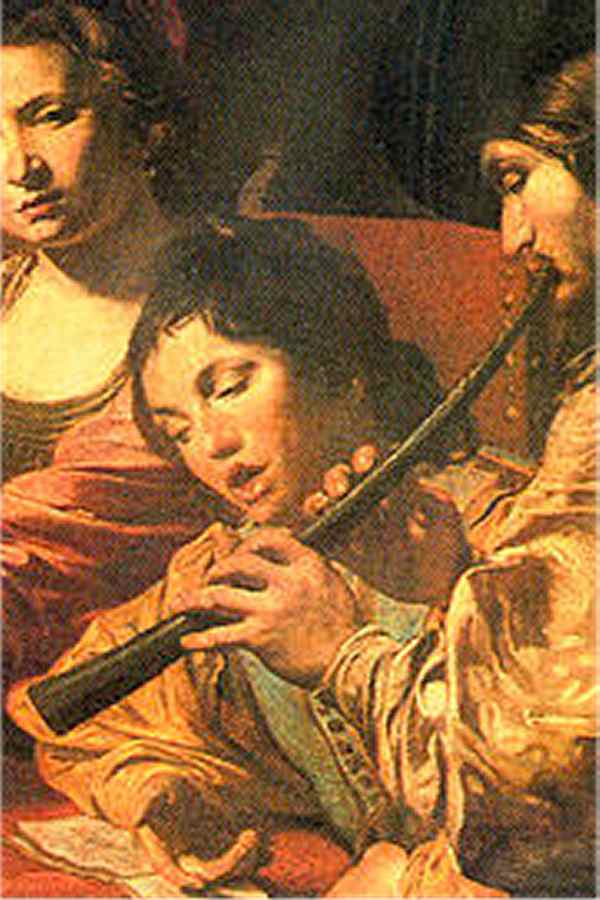

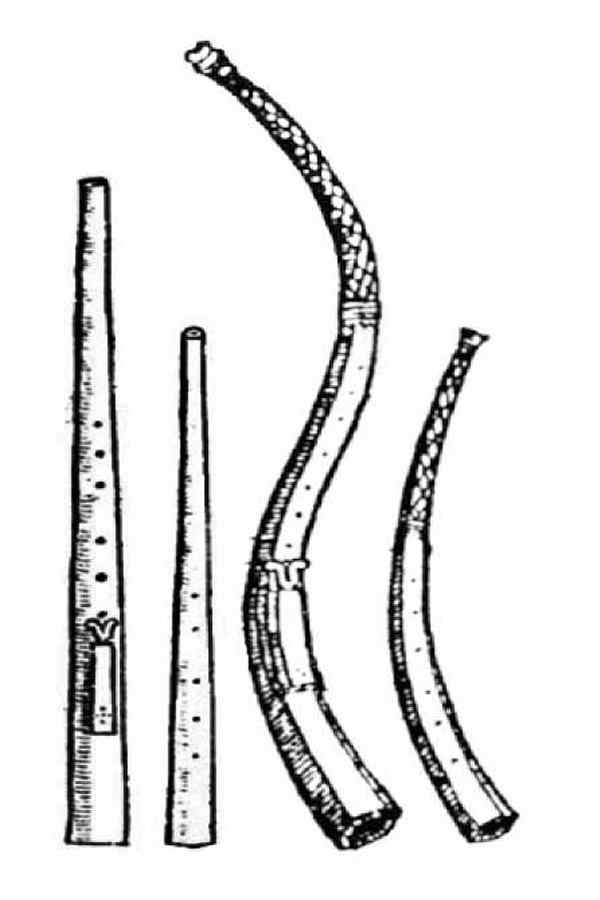
ein beliebtes Melodieinstrument
The zinc or cornetto was very popular in the music of the Renaissance and the early Baroque as a haunting melodic instrument and only lost its importance with the advent of the violin in the 17th century.
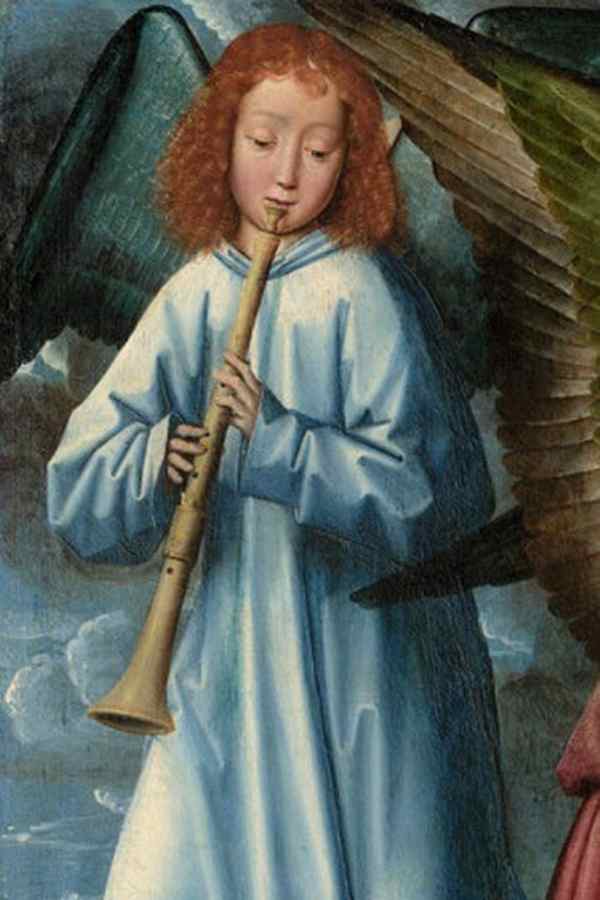
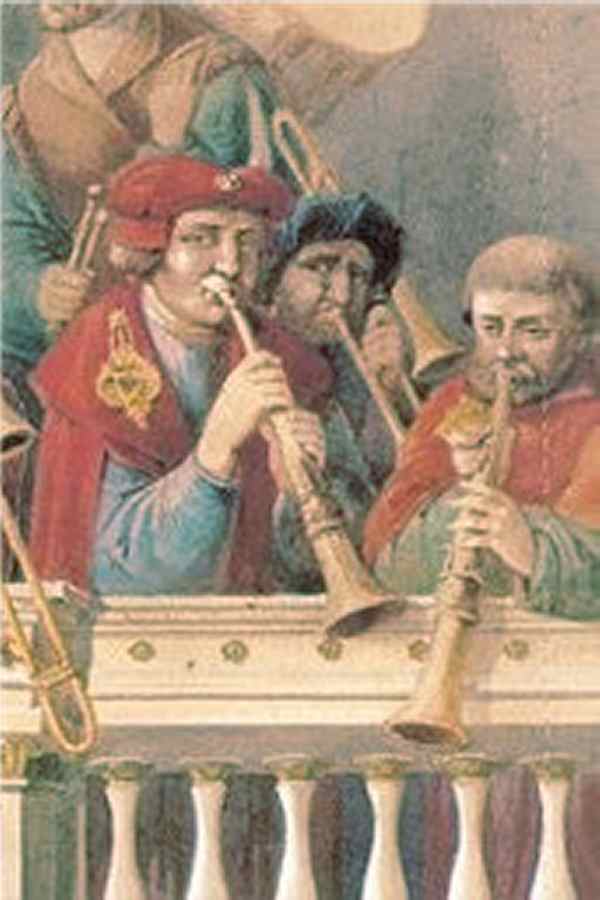


Durchsetzungsstark in jedem Ensemble
With its sound rich in overtones, the double reed instrument known as the bombarde or shawm stands out in every ensemble and has also been combined with brass instruments.
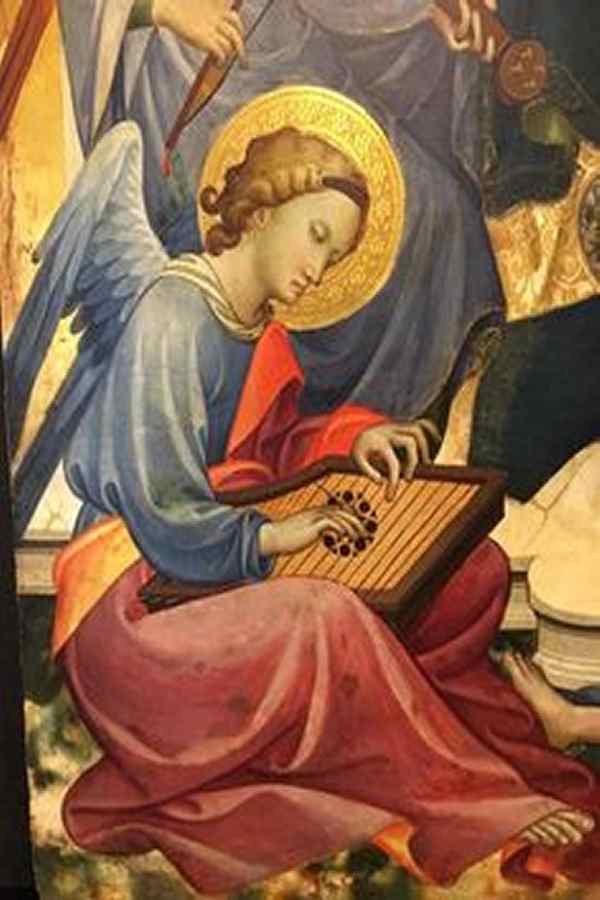


ein gezupftes Saiteninstrument
The psaltery is seen as the forerunner of the zither and dulcimer, but also of harpsichord and virginal. Technically speaking, it is an instrument capable of chords and polyphony. Due to the way it is played with plectrum or mallets, it is mainly used in this recording as a melodically played component of mixed ensembles.
Both for the sole accompaniment of a singer or instrumental soloists, as well as as part of a mixed ensemble, one recognizes the use of chordophones in many representations of the visual arts, i.e. instruments that are able to play polyphonically.
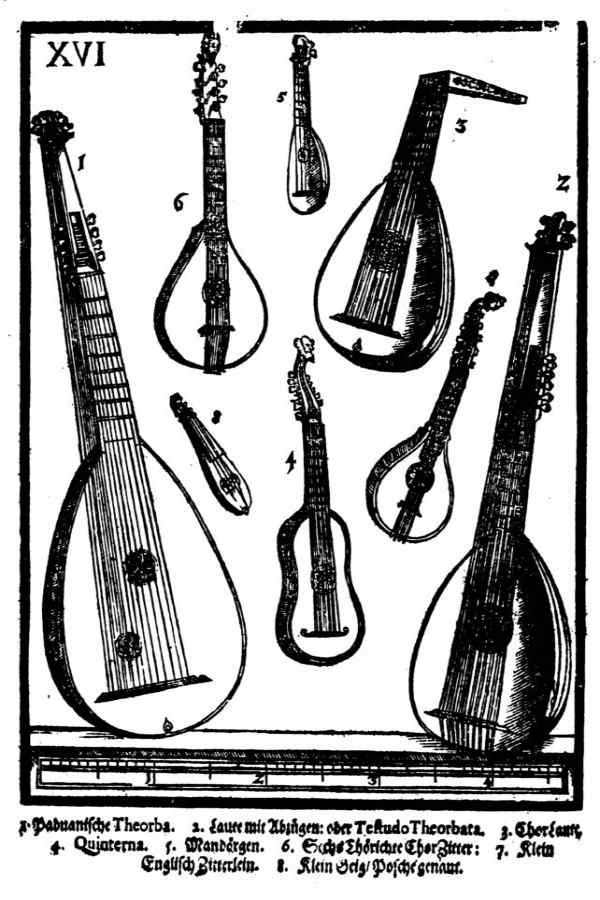


oft abgebildetes Begleitinstrument
In many illustrations from the Renaissance, the lute is often shown as an accompanying instrument for singers or other melodic instruments. In addition to the chordic summary of voices not sung, details or entire sections of the polyphonic movement can be adopted on the lute.
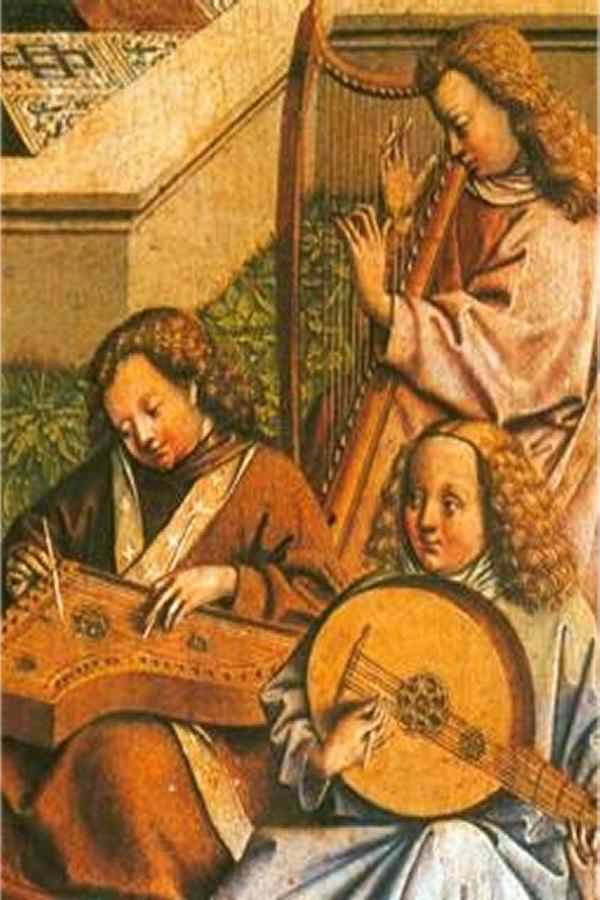
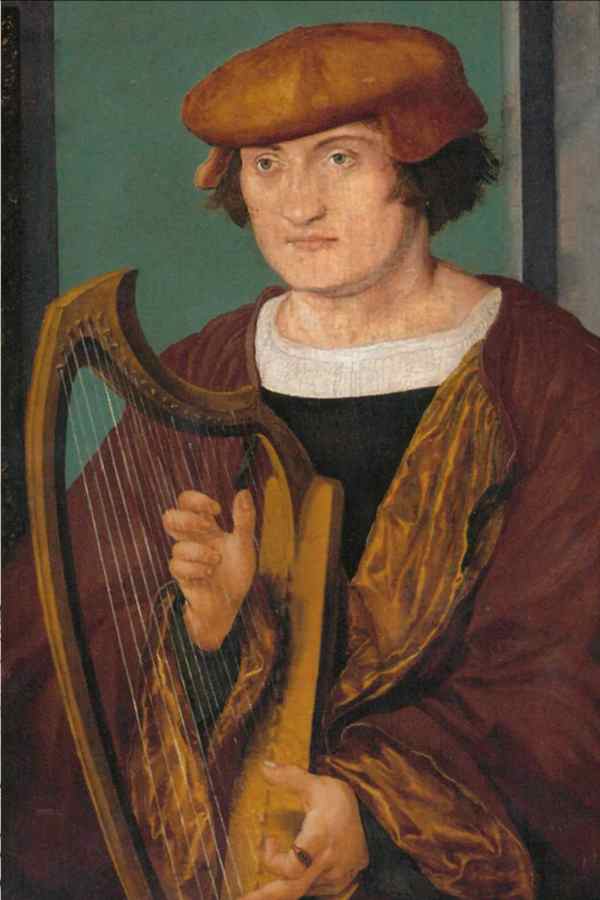


another plucked string instrument
Even if not as often as the lute, the harp is also documented in various historical paintings as an accompanying polyphonic instrument. The renaissance harps are significantly smaller than those used today
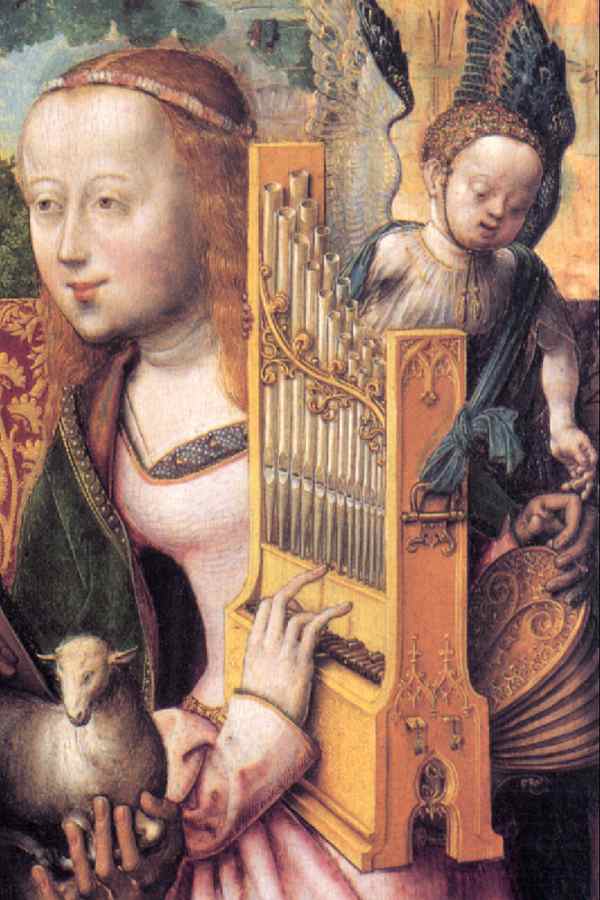
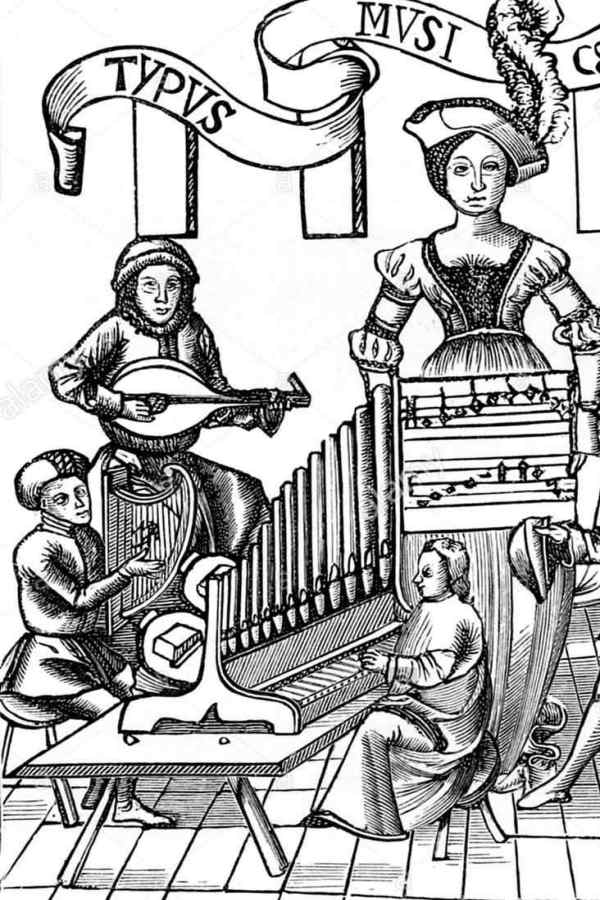


Organ in the private room
The portative, which already appeared in the Middle Ages and is documented in many illustrations, has apparently hardly been used in clerical contexts despite its relationship to the organ. As a polyphonic instrument, however, it can take on tasks that include accompanying and replacing other voices.
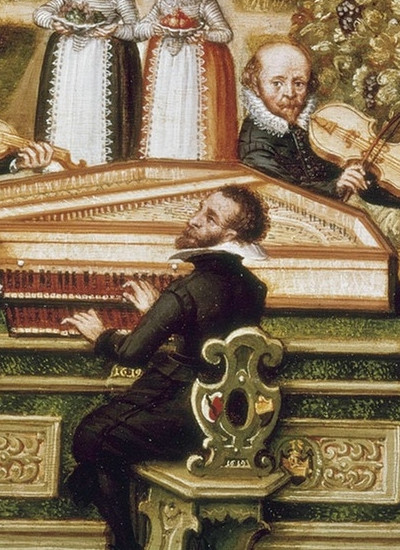
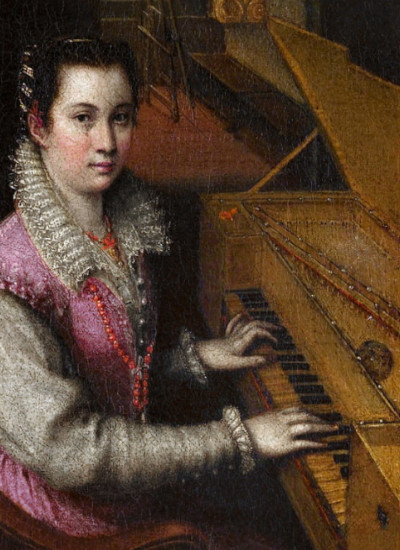


Plucked Instrument with Keys
The harpsichord, invented in the 14th century by the Viennese mathematician, astrologer, physician and organist Hermann Poll, reached its first heyday in the Italian Renaissance. In addition to the role of accompaniment, it also developed its own demanding repertoire.